- What it is and how it works
- The benefits of implementing it
- Companies that offer it
Let’s dive in!
What is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation is the process of replacing repetitive tasks with automated warehouse systems.
The goal of warehouse automation systems is to eliminate labor-intensive and time-consuming duties.
Doing so, in turn, frees workers up to focus on more value-added tasks, like quality control.
Overall, there are two types of warehouse automation:
- Digital automation
- Physical automation
Digital automation relies on software and electronics to reduce manual processes and improve the focus on customers and vendors.

A warehouse management system (WMS) is an example of digital automation software.
These systems can replace manual inventory tracking while providing more information to customers regarding their order status, thereby improving customer service.
On the other hand, physical automation refers to using warehouse automation equipment to reduce employee labor.

An example of physical automation is automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
These machines can transfer goods within an automated warehouse without the physical effort of a human employee.
The trends that we cover below include a mix of both digital and physical automation.
What are the Benefits of Warehouse Automation?
Every warehouse manager knows that warehouses are expensive to operate.
According to a 2018 report from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, a typical warehouse costs more than $3.7 million in labor expenses annually.
And this total doesn’t even include other expenses like health insurance, overtime, unemployment insurance, etc.

Ultimately, that’s the key benefit of warehouse automation: Lowering your operating expenses.
You may be wondering: How does warehouse automation impact efficiency?
The answer is that by adopting automated systems, warehouses can:
- Reduce human error
- Minimize labor
- Enhance material handling coordination
- Improve workplace safety
- Boost inventory control
- Improve customer service
These benefits will help improve efficiency and productivity while also cutting costs.
Implementing Warehouse Automation
Implementing warehouse automation involves a strategic and phased approach to ensure success and maximize benefits. Below is a detailed roadmap highlighting key steps, challenges, and solutions for transitioning to an automated warehouse.
Preparation and Planning

Before diving into automation, careful preparation is critical. Start by assessing your current warehouse operations to identify inefficiencies and areas where automation can provide the most value. Key preparation steps include:
- Conducting a Feasibility Study: Analyze your warehouse layout, infrastructure, and existing software systems like Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). This helps ensure compatibility with new automation solutions.
- Defining Goals: Establish clear objectives, such as boosting efficiency, reducing human error, or streamlining warehouse operations. Align these goals with your supply chain strategy.
- Budget Planning: Develop a comprehensive budget covering automation systems, software, workforce training, and ongoing maintenance.
- Involving Stakeholders: Collaborate with warehouse managers, supply chain executives, and technical support teams to gather insights and secure buy-in across all levels.
Selecting Automation Solutions

The next step involves choosing the right hardware and software for your warehouse environment. Tailor solutions to fit your operational needs and goals:
- Hardware Solutions: Consider automated material handling equipment, automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to optimize space usage and streamline operations.
- Software Integration: Ensure seamless integration between automation systems and existing WMS, ERP, or Transportation Management Systems (TMS). This enables accurate picking, inventory management, and real-time performance monitoring.
We will cover more automation solution trends in detail later in this article.
Pilot Programs and Phased Implementation

Avoid abrupt transitions by introducing automation gradually:
- Run Pilot Programs: Test automation solutions in a controlled environment to identify potential issues and refine processes.
- Phased Approach: Implement automation systems in stages, focusing on high-impact areas first, such as order fulfillment or material handling. This minimizes disruptions to your operations.
Workforce Training and Change Management

Automation success depends on how well your workforce adapts to new technologies. Address potential resistance by:
- Investing in Training Programs: Educate employees on using automated systems and highlight how automation can enhance their roles rather than replace them.
- Fostering Collaboration: Promote human-robot collaboration to integrate automated systems into the warehouse floor effectively.
Overcoming Challenges

Implementing warehouse automation can come with obstacles, but proactive planning can mitigate these:
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Work with experts to ensure new systems are compatible with older software and hardware.
- Physical Plant Upgrades: Address structural changes, such as dock and storage capacity improvements, to support automation solutions.
- Workforce Adaptation: Encourage an open dialogue about changes, emphasizing the benefits for employees and the company.
Monitoring and Optimization

After implementation, ongoing monitoring and optimization are essential:
- Performance Monitoring: Use data management tools to track efficiency gains and identify areas for further improvement.
- Continuous Support: Maintain systems through regular updates and technical support to ensure long-term success.
By following these steps, businesses can create a streamlined solution that boosts efficiency, reduces labor shortages, and optimizes warehouse operations. A well-implemented automation strategy not only enhances the warehouse environment but also strengthens the entire supply chain.
13 Warehouse Automation Technology Trends
Warehouse Management Systems
Warehouse management systems (WMS) are software applications to help with day-to-day warehouse operations.
These systems allow you to control, monitor, and optimize the key functions of your automated warehouse.
That includes:
- Tracking inventory.
- Directing picking, packing, and shipping activities.
- And even coordinating material handling equipment.
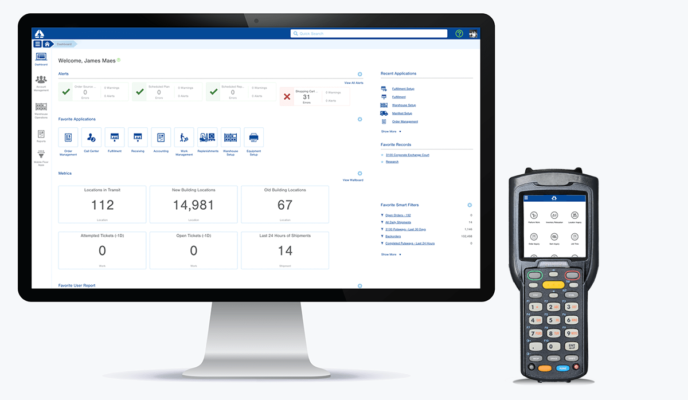
The main purpose of these systems is to ensure that warehouse materials move most cost-effectively and efficiently from the time they enter the warehouse until they leave.
Some of the benefits of using warehouse management systems include:
- Lower labor costs. A WMS can identify the best workers for the most important tasks. It can even generate schedules automatically to reduce labor allocation guesswork.
- Improved inventory management. Warehouse management systems can track inventory in real-time. This helps avoid backorders and other supply chain issues.
- Better use of warehousing space. These systems can help reduce wasted space by dictating the best places to store inventory.
The following vendors sell warehouse management systems, either as comprehensive modules or standalone products:
Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots – or “cobots” for short – are designed to work side-by-side with human workers.
The purpose of using cobots is to reduce errors, increase operating speeds and efficiency, and free up time for other tasks.

A study by Darex, a drill and knife sharpener manufacturer found that cobots increase efficiency by 30%!
Cobots can be used in many warehouse operations, including packing, picking, palletizing, and inspecting.
Some of the major vendors for cobots include:
Automated Guided Vehicles & Autonomous Mobile Robots
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are self-guided vehicles designed to move across your entire automated warehouse with an onboard operator.
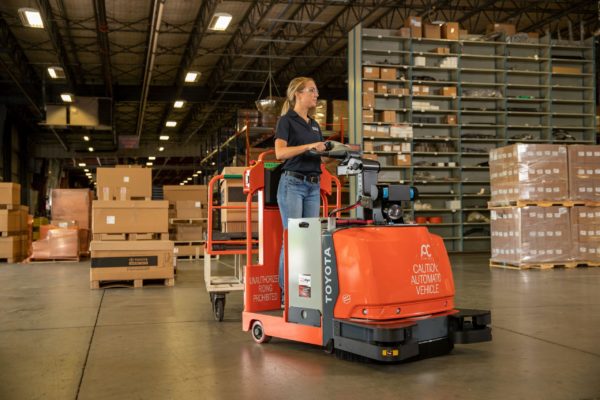

Unlike AGVs, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are designed to move automatically without an onboard operator.
This is done through sensors that interpret and understand their environment.
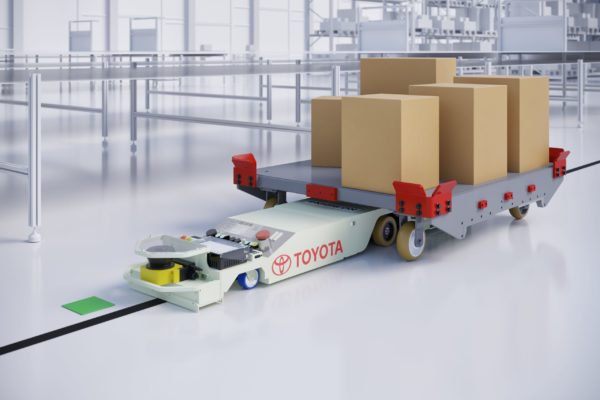

Overall, the purpose of using these mobile robots is to reduce repetitive actions, like moving cargo from one place to another.
This frees up workers to handle other, more skilled tasks.
Other benefits of using AGVs and AMRs include:
- Increased productivity and efficiency. They set the pace for employees and also keep associates on-task.
- Reduced labor. By taking care of navigation, these machines can reduce the labor allocated to handling materials.
- Less human error. Since they guide workers through each task, there’s better accuracy and fewer losses when handling materials.
- Better scalability. You can start with a few units and add them as your operation and needs change.
- Improved safety. Because of their in-built sensors and cameras, AGVs and AMRs can interpret their environment to avoid collisions.
AVG and AMR manufacturers include:
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems
Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) store and retrieve cargo in specific locations within a warehouse.
These systems are designed to follow established routes and get materials automatically.
As a result, they can eliminate the need for human workers to perform these tasks.
AS/RS systems can come in many different configurations, depending on the nature of a warehouse’s operations.
For example, they may consist of cranes, shuttles, vertical lift modules (VLMs), or carousels, among many others.
Overall, AS/RS technology has various benefits including:
- Lower labor costs. Since AS/RS systems take the manual labor out of picking and placing materials, there’s less need for human labor.
- Improved picking accuracy. By eliminating error-prone manual picking processes, AS/RS systems greatly improve accuracy.
- Maximized floor and vertical space. AS/RS systems offer high storage density. This is done by using compact storage, eliminating wasted aisle spaces, and taking advantage of vertical. space
The major companies that manufacture AS/AR systems include:
Wearables
Have you heard of wearable technology?
Some examples include augmented reality smart glasses, finger-trigger gloves, and GPS-tracking bracelets.
Each is embedded with smart sensors and designed to be worn by warehouse operators.
The devices are connected to the web and provide information to guide users in speeding up operations.
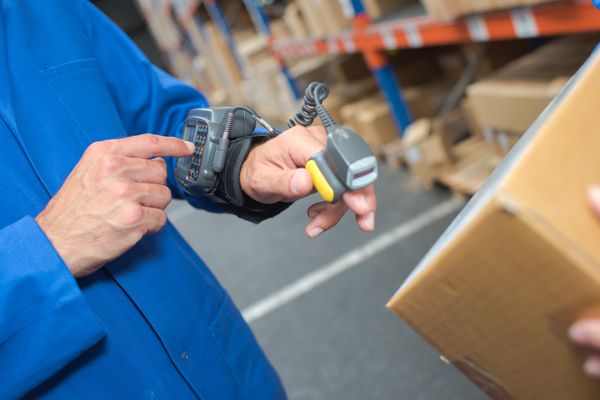

For example, they can show you how to stock, receive, navigate, ship, and even lift goods – all without taking your eyes off your work.
Other benefits associated with wearables include:
- Less distracted workers. Wearables eliminate the need for cumbersome paperwork or electronics, freeing workers to focus on order-picking tasks.
- Better efficiency. Wearables help reduce the number of “touchpoints” needed to complete tasks, allowing workers to do more in less time.
- Lower costs. Because workers can do more in less time, managers can reallocate labor to other, more critical areas to maximize their labor costs.
The major manufacturers of wearables are:
Predictive Maintenance
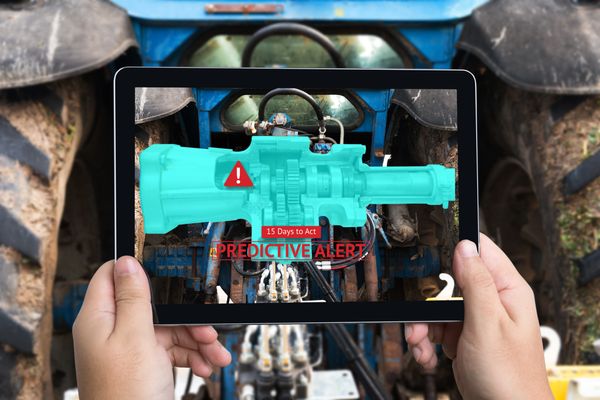
Most people are familiar with reactive maintenance.
This is when repairs are done only when equipment has broken down.
Conversely, predictive maintenance refers to monitoring equipment to detect possible defects before they fail.
These systems can then take the necessary prevention measures by automatically scheduling corrective maintenance.
A predictive maintenance software system connects and analyzes data using sensors like acoustic monitoring, infrared thermography, and vibration analysis.
They can integrate with business systems like enterprise resource planning (ERP) software and industrial controls.
Overall, predictive maintenance has many benefits for warehouses, including:
- Less downtime. Predictive maintenance will alert managers to equipment issues before they lead to downtime. A predictive maintenance system can reduce failures by up to 90%!
- Improved workplace safety. Equipment failures can cause serious safety issues. By preventing them in the first place, workers are better safeguarded.
- Increased equipment longevity. Equipment problems can balloon in severity if not corrected quickly. Since predictive maintenance alerts managers early, they can take care of those issues which can extend their equipment’s lifespan.
The major providers of predictive maintenance services include:
Fleet Management Systems
![]()
Fleet management refers to the monitoring and management of an organization’s vehicles.
The goal of fleet management is to ensure maximum productivity and efficiency while lowering operational costs.
It is estimated that 75% of fleet managers depend on fleet management software and vehicle telematics to run their daily operations.
These systems gather and analyze data from devices mounted on each vehicle, such as speed, engine run time, and fuel use.
This data can then be used to improve operations and reduce costs.
For warehouses, in particular, fleet management systems are often used to track forklifts.
And doing so can be beneficial in multiple ways:
- Tracking activity. Fleet management systems come with GPS locators. These let you track the location of your forklifts and operators easily within single or multiple warehouses. This can greatly boost your productivity and minimize errors.
- Protecting your equipment. Fleet management systems have security alerts that provide real-time updates concerning each forklift. You can use the updates to send messages to your operators for instant follow-up.
- Optimizing your workflow. With these systems in place, you can track the efficiency of your routes and find ways to improve them.
- Managing maintenance. By tracking hours of usage, managers can get a handle on when maintenance services are due.
Fleet management services can be obtained from reliable vendors like Unified Fleet Solutions and Toyota’s MyFleet.
Pick-to-Light and Put-to-Light Systems
Pick-to-light systems use light devices that direct workers on where to pull order items from storage.
First, the worker scans a barcode assigned to an order.
Next, lights on the racking show which items to pick for the order.

The idea is to eliminate the need for workers to manually view pick tickets, which can result in more errors and less efficiency.
On the other hand, put-to-light systems are simply the opposite of pick-to-light systems.
First, workers scan an order barcode.
Then, rack-mounted lights indicate where the material should be placed in storage.
The benefits of pick-to-light and put-to-light systems include:
- Increased productivity. It’s estimated that using pick-to-light systems can increase productivity by 30 to 50%.
- Improved picking accuracy. Workers no longer need to manually find item locations which results in a reduced chance of errors.
- Reduced training costs. These systems are simple and intuitive. Training can take as little as 30 to 45 minutes.
You can obtain pick-to-light and put-to-light systems from vendors such as:
Voice Picking
Voice picking is a method for using verbal commands to aid warehouse workers in fulfilling orders.
Typically, voice-picking systems are integrated with a warehouse management system or enterprise resource planning software.
When an order is received, the voice-picking system identifies the order’s requirements.
Then, they’ll verbally convey the information to workers, who receive the commands from a headset.
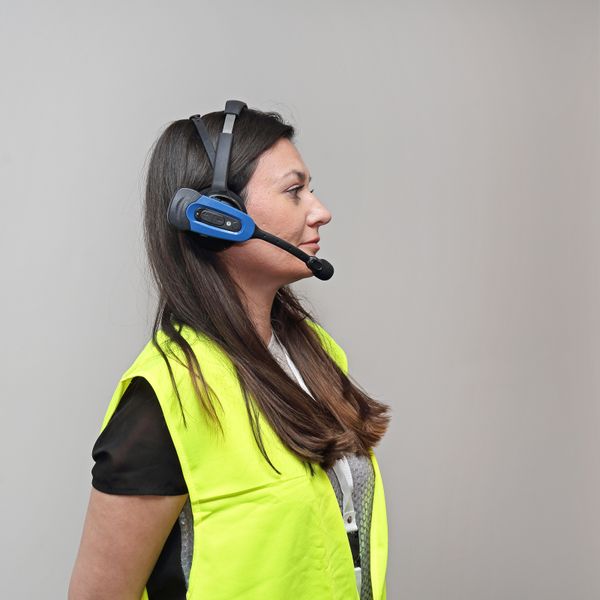

The worker is then directed to the item’s location to pick and told the quantity to pick.
Workers can also converse with the system to confirm locations and order quantities.
By adding a voice-picking system to your warehouse, you can enjoy many benefits including:
- Improved picking accuracy. Since voice picking takes much of the manual labor out of picking, order accuracy will be improved.
- Better productivity. Workers can focus solely on picking instead of juggling paperwork and various electronic devices.
- Improved safety. Since it’s hands-free, workers will be less distracted and thus less likely to cause or be involved in accidents.
The leading manufacturers of these systems include The Numina Group and Panasonic Mobile Solutions.
Automated Sortation Systems
Automated sortation is a way of removing the manual labor element of identifying materials on a conveyor system and diverting them to specific locations in your warehouse.
These automated warehouse systems use various technologies, including barcode scanners and sensors.
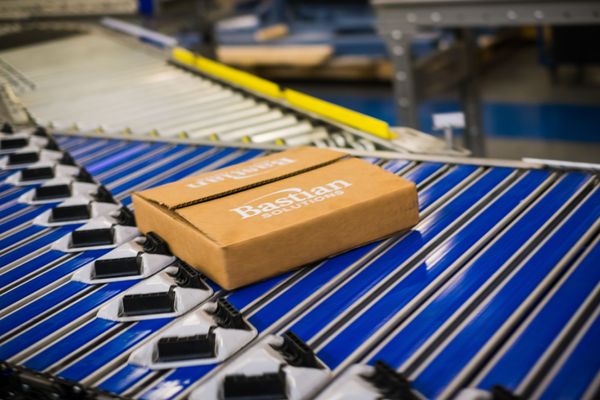

Automated sortation systems can be of two types, generally:
- Case sorters, which handle whole totes
- Unit sorters, which handle individual items
Under these two categories, many sortation systems exist that can tilt, pivot, push, or drop items on a conveyor to divert them where they need to go.
The benefits of using automated sortation in your warehouse include:
- Less reliance on labor. Automating sortation can be a way to cope with increasingly small labor pools.
- Faster processing. These systems can work faster and longer than humans can, which improves productivity and efficiency.
- Better order accuracy. Taking the manual guesswork out of sorting will reduce errors and ultimately result in happier customers.
Some reliable vendors of these systems include:
Industrial Internet of Things
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the network of connected devices in an industrial setting.
This can include many technologies we’ve covered, like warehouse management systems, predictive maintenance software, and automated guided vehicles.
This interconnected “web” allows for interacting, sharing information, and ultimately providing ways to improve coordination and efficiency.

The benefits of outfitting your warehouse with the Industrial Internet of Things include:
- Better efficiency and productivity. IIoT can help warehouses find gaps in operations that impair efficient operations.
- Lower costs. Better communication between equipment and software can help reduce issues like unplanned downtime and inefficient use of equipment.
- Better decision-making. By providing more data, the IIoT can help warehouse managers make more informed decisions about where to allocate limited resources.
You can get the IIoT in your warehouse from:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are changing warehouse automation and logistics.
AI-powered robots can do tasks like sorting, picking, packing, and organizing inventory more efficiently.
AI-driven sensors and cameras also help track inventory in real time, improving inventory management and reducing losses. This is turning regular warehouses into high-tech distribution centers and is very important for the industry as there is a shortage of warehouse workers, and the cost of labor is increasing.
Researchers at MIT have created a deep-learning model to make robotic warehouses more efficient. This is especially useful in industries like e-commerce and car manufacturing. The model helps by using the following:
- Traffic Congestion Management: Using traffic management methods to coordinate robots.
- Neural Network: Storing information about the warehouse to make accurate predictions.
- Efficiency Improvement: Finding the best areas to reduce congestion, making the whole system work better.
- Group Division: Splitting robots into smaller groups so they can be managed more quickly by traditional algorithms.
- Computational Efficiency: Looking at all the robots together to handle computational limits well.
Here are some companies that offer Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (ML) solutions specifically for warehouses:
Pallet Shuttle Systems

The Pallet Shuttle system is a high-density storage solution that uses electric shuttle retrieval systems to move along rails inside a storage channel.
These systems use a WiFi-connected tablet, operated by an operator, to control the shuttle and place the load in the first available spot. Since forklifts don’t need to enter the lanes, pallet shuttle racking helps maximize storage capacity by allowing for deeper pallet racks and minimizing wasted space.
Key Features and Advantages:
- Efficient Automated Storage: Each channel can hold a different item, allowing for more variety. These systems can store pallets in lanes up to 131 feet deep, with minimal space between levels for high-density storage.
- High Productivity: This system speeds up the flow of goods in and out of the warehouse. The shuttles move at high speeds and fill or empty a whole lane with one command.
- Safety and Cost Savings: The design removes the need for forklifts inside the racks, reducing the risk of accidents and damage. This lowers maintenance costs. Built-in sensors and advanced features make the system easy to use and maintain, saving time and money.
- Versatility and Scalability: These systems can work in different modes, like LIFO or FIFO, and can be easily expanded by adding more shuttles. It can handle different types of pallets and operate in temperatures from -22° to 113° F.
- Advanced Control and Monitoring: The shuttles can be controlled and monitored with a tablet, including inventory tracking so operators can always see how many pallets are stored.
Here are some companies that offer a pallet shuttle system: