Are you trying to decide between equipment refurbishment or reconditioning? Well, you have come to the right spot.
This article is your ultimate guide to equipment refurbishment vs reconditioning.
Here, you will discover:
- The differences between forklift refurbishment and reconditioning.
- Which is the right choice for you?
- How much you can expect to pay for each?
- And more!
We also answer some frequently asked questions about equipment refurbishment vs reconditioning.
Let’s dive in!
Equipment Refurbishment Defined
According to the Merriam-Webster online dictionary, refurbish means sprucing up something cosmetically or superficially, like renovating to return it close to working condition.
So, what is equipment refurbishment?

Equipment refurbishment is reassembling and replacing components and parts to restore them to their original manufacturer’s working condition.
And Refurbished equipment meaning?
Refurbished equipment is those serviced to offset the wear and tear associated with its daily use and return it as closely as possible to its original condition.
The process of refurbishing equipment is sometimes called reconditioning.
Equipment reconditioning is taking worn or damaged parts and replacing them to restore the equipment to its original condition.
Generally, refurbishment is a less comprehensive operation compared to reconditioning. But the two terms are often used interchangeably.
What Equipment Refurbishment Entails
Usually, a used machine may or may not necessarily be effectively maintained or serviced. So, while it might appear shiny and new on the outside, especially after a thorough cleaning, it may still have functional issues internally.
Refurbishment means that a machine is keenly disassembled and inspected and that any worn or damaged parts and components are either repaired or replaced.
Learn more here about forklift repair services.
The equipment is then put back together, aiming to restore it to as close to its original “as new” condition as possible.

Differentiating refurbished equipment from a new one is difficult without looking at the dashboard details.
Why Refurbish Your Equipment
What are the benefits of equipment refurbishment?
Refurbishing equipment is a mix of cost savings, equipment availability (whether new or used), and the ability to refurbish equipment, considering component availability.
So, here are the key benefits of equipment reconditioning
1. Cost Savings
Cost savings is an obvious benefit of refurbishing equipment. Refurbishing can save as much as half of the cost of a new machine. Companies can then put the saved funds to profitable use in other business areas.
Refurbishing equipment is a sensible response to economic pressures in any company. Why?
Because refurbishing the equipment means that you will get the same performance and reliability you get with new equipment, but at a fraction of the cost.
In addition to the cost savings, refurbishment increases equipment resale value and can provide tax benefits to a business. It is possible to recapitalize a refurbished asset on a depreciation schedule at half the value of a new machine.
2. Eliminates Potential Downtime

Refurbishing eliminates the potential downtime and worries resulting from buying a used machine “as is.”
It ensures that company operations run smoothly with minimal disruption. It allows operators to keep working even when facing delays in lead times, ensuring continuous operations.
And if you are working with a reputable workshop or dealer like Conger, you can expect performance similar to brand-new equipment.
3. Ensures Equipment Availability

Applications may require specialized equipment to fulfill their operations. For example, paper mills often use higher-capacity indoor cushion tire forklifts with paper roll clamps.
These specialized trucks are not produced in large quantities each year, leading to supply and demand challenges.
When equipment is wearing down, maintaining operations becomes a challenge. In such cases, consider how and if you can obtain replacement equipment. However, a supply and demand imbalance might make obtaining the needed equipment difficult.
In that case, equipment reconditioning or refurbishing becomes an option. It will offer quicker lead times compared to manufacturing. Meaning you can get the equipment faster, making it a cost-effective solution.
You also avoid the risks of buying a used machine that can be faulty or non-functional.
4. No New Operator Training

When you refurbish your equipment, you should not have to spend time and money training operators to use a different machine, new or bought secondhand. The operators already know how to use the reconditioned equipment.
5. New Innovations and Cosmetic Upgrades

When you refurbish your machine, you can install innovations and technology to enhance your productivity and boost your output.
In addition, most equipment rebuilding processes involve cosmetic upgrades, so your equipment will look shiny and new.
When to Refurbish Your Equipment
The engine, transmission, hydraulic components, tires, chains, and other parts of the vehicle are the components that are most likely to wear out or experience breakdowns over time. For many forklift trucks, breakdowns tend to occur around the 10,000-hour mark.
At that point, the truck’s components can show signs of wear, impacting the operation and leading to higher maintenance costs. It is necessary to begin replacing items like hydraulic seals, transmission seals, and engine gaskets.
This situation can call for equipment refurbishment or reconditioning.
Refurbishing equipment, when done by qualified professionals at the appropriate time and for the correct machine, offers substantial cost savings compared to purchasing a new one.
A good service or refurbishment center will work closely with you (or your business) to determine when equipment refurbishment is most appropriate.
But to achieve cost savings, you should know when refurbishment is the right choice.
The five factors to consider about equipment refurbishment are:
- Financial sense
- Type of equipment.
- Size of the fleet.
- Age of the equipment.
- The structural condition of the equipment.
Let’s discuss them in detail below:
1. Financial Sense

One crucial factor to cover is when it makes financial sense to recondition equipment.
Examine the economic and useful life of the forklift to determine how much time is left. Then, calculate how much time you can get out of the lift truck and weigh that against other options, like replacing it with new or used equipment.
Finally, consider lead times, availability, capital expenditures, financing options, and other factors to make an informed decision.
In many cases, reconditioning the forklift machine will be more cost-effective than buying new or used equipment.
Here is an example of reconditioning vs buying a new forklift:
Let’s consider a scenario with a forklift. Reconditioning the forklift might cost $50,000 while purchasing a new forklift could cost $100,000.
Suppose the forklift has a known lifespan of ten years. If you replace it with a new one every ten years, the annual cost would be $10,000. Reconditioning, however, could provide an additional two to four years of usage, which brings the cost per year to about $12,500, making it almost a wash financially.
The advantage is that you get to use the forklift around eight months earlier than if you were to order a new one, which often has long lead times. The same applies when searching for used equipment, especially for specialized items that may not be readily available.
2. Type of Equipment
With the current market structure, refurbishment is cost-effective only for mid-sized or large equipment, such as articulated haulers, wheel loaders, and excavators.
Usually, smaller machines like compact equipment are not as suitable for equipment refurbishing. Why?
There are two major reasons:
- The market for used equipment is much stronger for compact equipment than large equipment because they have a higher resale value. It is easier to find someone who wants to buy old compact equipment, which makes equipment refurbishing for heavy equipment a good choice.
- Relative to large equipment, the prices of components for compact equipment is a higher percentage of the overall cost. It is difficult for service centers and dealers to refurbish this equipment at an attractive rate compared to buying new.
Many businesses prefer heavy equipment restoration because of the costs of buying new ones.
3. Size of the Fleet
Equipment refurbishment can take up to 60 days. So, as an equipment manager, you must plan for downtime.
If your fleet is small and relies on that equipment to operate the business, you need to weigh the options accurately. For example, compare how much a refurbishment will save versus the loss in productivity by up to 60 days of refurbishment.
The decision is easier if you have a large fleet and can plan for the downtime and compensate with the rest of the equipment.
4. Age of the Equipment
Although it can be convenient to say that equipment is best suited for refurbishment at a certain number of hours, such a statement is too general. When to refurbish a machine depends on its type, age, and tasks.
We measure the age of material handling equipment in terms of hours. Most forklifts might need refurbishment after 10,000 – 15,000 hours. But this is also determined by the applications the machine has gone under and its current condition.
Learn more here about common forklift repairs.
For example, Counterbalance forklifts are typically good candidates for refurbishment around the 12,000- to 15,000-hour range. If the equipment has worked in a harsh application, such as a rock quarry face, 12,000 hours would be appropriate to inspect the machine.
In other applications, such as warehouses and waste handling sites, it is not uncommon for a forklift to run well after 15,000 hours without changing the engine/transmission. Consider inspecting them around this time to prevent unexpected breakdowns and downtime.
Similarly, an articulated lift’s lifespan depends on its operation. If the truck has been handling 40-ton loads in and out of steep, rough quarry roads, 8,000 hours is a good time to consider refurbishment. In milder environments, the lift can typically run for about 12,000 hours before considering refurbishment.
Excavators and other large forklifts do not have a clear-cut timing of refurbishment. Their hydraulics often require repair or replacement around the 8,000-hour mark, whereas other engines can run up to 12,000 hours. So, before considering refurbishment, you can weigh the options and see if it is cost-effective.
5. Structural Condition of the Equipment
Refurbishment involves replacing nearly every part or component except for the equipment frame. That is why the structural strength of the equipment is crucial in determining whether to refurbish or purchase new.
Typically, a newer machine with many operation hours is an excellent candidate for refurbishment.
However, an older machine that has accumulated the same number of hours over a long period is more likely to have structural problems. This factor makes it less suitable for refurbishment.
A good dealer or refurbishment center will work closely with the equipment owner to determine when refurbishment is appropriate.
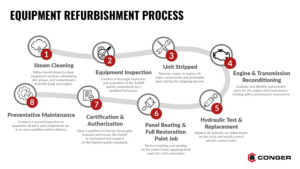
The Equipment Refurbishment Process
There is a process to follow during equipment refurbishment.
Let’s explore:
1. Steam Cleaning
The process for equipment refurbishment starts with a steam cleaning for thorough and effective washing.
Steam cleaning involves using steam forced onto a surface to clean the equipment to remove dirt, grease, and other items from the body and engine.
Steam cleaning is thorough because when steam contacts a surface, tiny vapor molecules can enter pores and clean the surface effectively. The vapor removes all dirt, grease, bacteria, detergents, and particles that do not naturally belong on that surface.
2. Equipment Inspection
After cleaning, the next step in the Equipment Refurbishment process involves a skilled technician inspecting and evaluating the forklift and its parts.
The inspection encompasses three main categories:
- Visual: The Examination of easily visible aspects such as paint condition, tire tread, operator seat and seat belts, floor mats, and other visible features.
- Mechanical: Inspection of major mechanical components such as the drive line, engine, transmission, axles, brakes, differential unit, and other critical parts.
- Electrical: Assessment of electrical and mechanical components, often utilizing computer diagnostics to ensure thorough evaluation.
The inspection results give a detailed look at the equipment, inside and out. The refurbishment process from here varies based on what the service center finds.
For this reason, finding a qualified and efficient service center or dealership for your equipment inspection is crucial.
The dealer will show you the inspection results and let you choose what refurbishment works best for your situation: flexible repairs or a complete overhaul.
Before you settle on a service center, consider the following:
- Check if they are certified by the equipment brand or a refurbishment center.
- Visit them and get a refurbishment quote before authorizing any work.
- Ensure they have standards for procedures, facilities, and staff.
- Check if they offer standard inspection and testing criteria for forklift machines.
- Verify the credentials of the technicians; they should be master-level technicians.
3. Unit stripped
Next, the equipment should be stripped down, with all major components and parts, inside and out, removed, repaired, or replaced. This process should executed with careful attention to the critical components
This process includes the following:
- Tires, where applicable.
- Mast
- Bearings
- Chains
- Lockout / Tagout
- Hydraulics
- hydraulic piping
- Bushes
- Seals
- Seat
- Forks
- Front and rear lights
- And more.
These newly installed fittings should undergo testing to ensure proper functionality. Make sure the service center follows a consistent equipment repair procedure for efficiency.
4. Engine and transmission reconditioning
Next is to go through the engine and transmission and identify replacement parts.
The technicians should start by evaluating the engine and transmission performance.
Have them run some stall tests on the transmission to see if any internal issues need addressing. Next, they should do compression and leak-down tests on the engine to see where (if there is an issue) and determine how extensively the engine needs work.
In the engine and transmission inspections and tests, the technicians can reseal some seals, such as front and rear crank seals.
Additionally, technicians should perform general maintenance tasks such as replacing the oil pan, valve gasket, and cover gasket, installing new water pumps, and other necessary activities.
On the transmission, the technicians can reseal components such as the torque converter and the torque converter seal itself. They should reseal both the output seal and the torque converter in the transmission to prevent potential leaks.
Once all of these are in order, the compression test is complete.
5. Hydraulic Test and Replacement
The technician’s next step is to replace every hydraulic or rubber hose on the truck, install a new hydraulic control valve, and reseal every cylinder. This precautionary process is necessary because hydraulic systems can heat up, and if they are old, they may develop leaks. Replacing all those components gives the machine a new life, extending its longevity.
6. Panel Beating and Full Restoration Paint Job
In addition to the engine and transmission seal, the technicians and service center will do a restoration paint job on the equipment. This process includes detailed work like cleaning and sanding the entire frame, followed by a fresh coat of paint. The goal is to make the vehicle look as new as possible and properly function.
This process breaks down to include:
- One layer of primer paint.
- Body fill all dents and damaged equipment body components.
- Final coats painted. All original colors.
- New tires fitted or tire repair.
- All major components were replaced and fitted.
- All equipment perishable parts were replaced and fitted.
- Steering adjustment.
- Seat replacement to your preference.
- Any other important part and component fitted.
7. Certification and authorization
Before delivering the refurbished forklift, a qualified technician must evaluate it and ensure it is thoroughly overhauled and repaired for the best quality.
A fully accredited inspector examines the forklift and gives it a certificate confirming successful exam completion.
The inspector then gives quality insurance with a pre-delivery inspection report, ensuring the machine is delivered per OEM standards and in perfect condition.
8. Preventive Maintenance
One more thing. The equipment is then Load-tested and made ready for delivery.
But before that, preventive maintenance has to be done. A second inspection is needed to ensure all the parts and components are as new as possible.
The forklift equipment will then undergo preventative maintenance. This procedure includes maintaining fuel filters, changing hydraulic filters, changing hydraulic oil, changing the differential fluids, putting on new bushings on the steer axle, new alternator, replacing the tires with new ones, and overall condition inspection.
Learn more about the forklift maintenance guide here.
The idea of refurbishing is to ensure the equipment leaves the service center as functional as new.
Common Equipment Refurbishment Questions
What is Equipment Refurbishment?
Equipment refurbishment refers to restoring, repairing, and upgrading used or worn-out equipment to a condition that closely resembles its original state. Sometimes, equipment refurbishment can enhance the machine by incorporating innovations and technology.
What is the Difference Between Repair and Refurbishment?
Repair and refurbishment are processes used to restore equipment to a functional state, but the two have key differences.
Repair refers to fixing or replacing specific issues or damages in equipment parts/components to bring them back to their normal working condition. It focuses on addressing the problem that caused the equipment to malfunction or become inoperable. Repair does not significantly alter the overall appearance or functionality of the equipment.
Refurbishment involves thoroughly assessing, restoring, and improving equipment to a state that resembles its original condition. The refurbishment aims to fix existing issues and enhance the overall performance, appearance, and functionality. This process typically includes cleaning the equipment, replacing the worn-out parts, upgrading components, and conducting thorough testing to ensure the equipment meets quality and safety standards.
What Are the Benefits of Equipment Refurbishment?
Equipment refurbishment offers several benefits, including:
- Cost Savings: Refurbishing equipment is often more cost-effective than purchasing new equipment, especially for businesses on a budget.
- Eliminates potential downtime: Refurbishing eliminates the potential downtime and worries linked to the longer lead times involved in buying a used machine “as is.”
- Environmental Impact: Extending the lifespan of equipment reduces the need for manufacturing new items and helps decrease the environmental impact associated with producing and disposing of new equipment.
- Availability: Some equipment may no longer be in production or is hard to find, making refurbishment a viable option to keep using essential tools or machinery.
- Customization with innovations and technology: During the refurbishment process, upgrades and modifications can manufactured to tailor the equipment to specific needs or to incorporate new technologies.
How Long Does a Full Refurbishment Take?
A refurbishment can take 10 to 12 weeks or up to 60 days.
However, the duration of a refurbishment can vary widely depending on several factors, such as:
- The type of equipment
- The extent of repairs and upgrades
- The availability of replacement parts
- The expertise of the refurbishment team
How Many Steps Are There in the Refurbishment Program?
There is no fixed number of steps involved in an equipment refurbishment process. The key ones are:
- Steam Cleaning: Your forklift equipment undergoes thorough steam cleaning.
- Equipment inspection: A qualified technician performs an inspection evaluation of the forklift equipment and its components.
- Disassembly: The unit is stripped, with all internal and external components removed for repair or replacement, focusing on critical components noted during evaluation.
- Repair and Replacement: Damaged or worn-out parts are repaired or replaced with new components. Potentially involving fixing mechanical, electrical, or electronic components, depending on the type of equipment.
- Engine and Transmission Reconditioning: This can include filter replacements, hydraulic and fluid changes, and compression tests.
- Paintwork and sanding: Sanding of the forklift, if necessary, filled to smooth out any imperfections before repainting, giving it a fresh appearance.
- Certification and authorization: An accredited inspector examines and certifies the forklift to ensure the refurbishment is completed effectively with the required standards.
- Preventative maintenance: Before the equipment is delivered, preventative maintenance is performed on the vehicle, ensuring that all perishable parts are up to date. Additionally, to ensure ongoing upkeep, a maintenance schedule is established.
What is the First Step of the Refurbishment Process?
The first step in refurbishment is visual inspection. A qualified and accredited technician inspects and evaluates the forklift equipment and its components. During this step, the technician evaluates the condition of the vehicle to identify any issues, defects, or areas that require improvement.
This initial evaluation sets the foundation for the entire refurbishment project. Its key actions and considerations include:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the equipment visually to identify visible damages, wear, and other issues that might affect its performance.
- Functional Testing: Test the equipment to determine whether it is operational and identify malfunctions or performance problems.
- Documentation: Document the current state of the equipment, noting the observed issues and any data related to its functioning.
- Scope Definition: Define the scope of work for the refurbishment; what repairs, replacements, upgrades, or enhancements are necessary or desired.
- Budget and Timeline: Establish a budget for the refurbishment project and set a timeline for completion, considering factors like replacement parts, labor costs, and potential unforeseen issues.
- Client or Stakeholder Communication: If the equipment belongs to a client or organization, communicate the assessment findings and the proposed refurbishment plan to ensure alignment and approval.
Conclusion

That is it: Equipment refurbishment definition, benefits, costs, and more.
Refurbishing your forklifts provides a cost-saving solution. It helps your company save money and survive challenging economic times.
![Equipment Refurbishment vs. Reconditioning [Differences, Benefits, Costs]](https://www.conger.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Refurbishment_Vs_Reconditioning_FeaturedImage-100-1.png)





