Curious about lithium forklift batteries?
Then you’re in the right place.
Because in this post, we’re going to cover everything you need to know about them!
That includes:
- Key differences between lithium-ion and lead-acid
- The major features, advantages, and benefits of lithium-ion
- What you need to be aware of before considering a switch to Li-ion
- Major lithium-ion forklift battery manufacturers
- How much lithium-ion forklift batteries cost
- And lots more…
Let’s dive in!
Is It Worth It to Buy Lithium Forklift Batteries?
The short answer is: If you are a medium to large-size operation running multiple shifts, lithium-ion forklift batteries could be a very good option for you.
Why?
Because even though lithium forklift battery prices are currently higher compared to lead-acid batteries, they offer a lot of cost-saving benefits in the long run.

Lithium forklift battery’s ROI is also often achievable within 36 months.
Overall, lithium-ion forklift batteries are 40% more energy efficient than lead-acid. And they’re 88% more efficient than diesel.
Lithium-ion batteries are designed to last longer, making them a good choice for operations where changing the battery is inconvenient.
They can also withstand extremely low temperatures without failing, making them ideal for outdoor applications.
Lithium-Ion vs. Lead-Acid Forklift Batteries
There are 2 basic power types (forklift batteries) for electric forklifts: lead-acid and lithium-ion.
But what’s the actual difference between these 2 technologies?
Lead-Acid Battery Chemistry
Lead-acid batteries have been the most common type of battery for a long time. Their technology goes back to the mid-1800s. Also called “wet cell batteries,” lead-acid forklift batteries are relatively inexpensive.
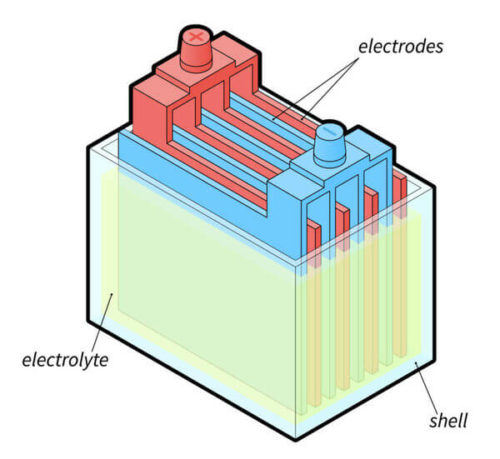
Lead-acid batteries generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction between lead plates and a mixture of 30 to 50% sulfuric acid and distilled water (called an “electrolyte solution”).
The components of lead-acid batteries include:
- Cells
- Bars
- Plates of lead dioxide
- Cables
- Electrolyte
To generate electricity, an electrochemical reaction occurs between the lead plates and the electrolyte solution.
The electrical ions flow from the sulfuric acid to the negative plate, generating electricity.
Lead-Acid Battery Charging
It takes longer to charge lead-acid batteries than it does lithium-ion. It’s mostly done through conventional charging, usually after a shift, using a low current for about 8 to 10 hours until it’s charged 100%. This longer charging is followed by 6 to 8 hours of cooling before using the battery again.

Conventional charging is mostly done overnight and is best for single-shift operations.
This also means lead-acid batteries don’t usually undergo opportunity charging. It can damage the battery quickly, wear it out quicker, and reduce its cycles.
Overall, lead-acid forklift batteries have a shorter lifespan: typically, 3 to 5 years (or between 1,000 and 1,500 charging cycles) under normal 40-hour week operations).
Lithium-Ion Battery Chemistry
Lithium-ion batteries have become more widespread in consumer electronics in the past few decades. Now, lithium-ion is becoming an increasingly popular forklift motive technology.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries are composed of the following:
- a cathode,
- electrolyte (lithium),
- anode,
- separator, and
- 2 current collectors (positive and negative).
To generate electric energy, different chemistries occur in lithium-ion batteries, with the most popular one for forklifts being lithium iron phosphate.
The anode and cathode store the lithium. When a lithium-ion battery is discharging, the electrolyte moves from the anode to the cathode through the separator carrying positively charged lithium-ions from the anode to the cathode.
When the battery is charging, the electrolyte liquid moves from the cathode to the anode through the separator, carrying negatively charged lithium-ions.
Lithium-ion batteries are easily charged through opportunity charging because they’re fast charging. This charging uses a specialized charger with a high current to charge the battery quickly.
Opportunity charging can be done on a need basis or when it’s most convenient, making lithium-ion batteries more efficient.
If maintained well, a lithium-ion forklift battery will last between 2,000 and 3,000 cycles or about 7 to 10 years of 300 workdays per year.
Lithium-Ion Forklift Battery Pros
Lithium-ion batteries can offer your operations increased efficiency.
If the conditions are right for the investment, there is available space for charging, and your budget allows, several key factors may lead you to adopt this energy solution.
Increased Productivity
Lithium-ion forklift batteries take less time to charge than lead-acid batteries, which also need time to rest before they can be used again.
A lithium-ion battery can get fully charged in less than 2 hours and does not require a cooling-off period like lead-acid batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries can be charged in 15-30-minute spurts, called opportunity charging, allowing you to charge them during lunch, breaks, or anytime the forklift is idle for a few minutes. This allows multi-shift operations.

In addition, lithium-ion batteries can last longer on a single charge than lead-acid batteries.
Compared to lead-acid batteries’ linear discharge curve, the lithium-forklift battery discharge curve is much flatter. This means that over a wide operating range, the voltage at the battery terminals changes very slightly, allowing the battery to hold more power even when almost fully discharged.
It can be used up to beyond 80% state-of-charge (SoC) but not to zero. When the SoC reaches zero, there may be a charge remaining in the battery, and further discharge may damage it.
With Li-ion, your fleet will benefit from lower downtime and increased productivity and throughput.
Opportunity Charging
Forklift battery charging is an important factor to consider.
You can top up lithium-ion forklift batteries during 15-30-minute breaks within the day (known as opportunity charging). While you can opportunity charge a lead-acid battery, it shortens the battery life.

Furthermore, lithium-ion batteries can fully charge in as little as 1 hour or a maximum of 2 hours. That’s 8 times quicker than a lead-acid battery, without the need for cooling down time.
This is why it’s possible for 1 lithium-ion battery to power three shifts. They store 4X more energy and are 30% more energy efficient.
Less Maintenance
Like forklift maintenance, forklift batteries also require maintenance.
If lead-acid batteries aren’t maintained properly, they undergo a chemical process called battery sulfation. This can cause them to break down. Thus, you must maintain their level of water and electrolyte, topping up the battery with distilled water regularly to maintain its health. Maintenance can be time-consuming and costly.

This is different in lithium-ion batteries, which require little to no maintenance.
Lithium-ion batteries don’t need to be topped with water and do not require any such frequent maintenance procedures, such as equalizing charging and cleaning.
They come equipped with sealed cells that you don’t have to wash or add water to keep the batteries operational. This also reduces maintenance labor and costs.
Also, depending on your operation you don’t have to remove or swap batteries within your workday because a Li-ion battery can remain inside the forklift longer.
No watering, removing the battery, or other maintenance also means no watering areas or maintenance areas, which saves facility and storage space.
Energy Efficient
Lead-acid batteries bleed energy while discharging, charging, or sitting idle, leaving only about 80% of the energy used for charging the battery available as the output. This makes lead-acid batteries energy inefficient and adds up electricity costs.
On the other hand, lithium-ion batteries are more energy efficient because they have minimal losses, leaving most of the energy used for charging available as an output, sometimes up to 99%.
So, lithium-ion batteries can help you reduce electricity costs because they provide more output owing to minimal energy losses.
Supports Multi-Shift Operations
If your operations last 16 or 24 hours a day, battery charging times are crucial for smooth operations.
Why?
A typical battery discharges in about 6 to 8 hours.
This is where there’s a key difference between lead-acid forklift batteries and lithium-ion forklift batteries.
A typical lead-acid battery requires about 8 hours to charge, followed by 8 hours of cooling. This is about 16 hours before the battery can be used again.
So, you may need 2 to 3 lead-acid batteries per forklift for a multi-shift operation or you’ll experience downtimes.
A lithium-ion forklift battery gets fully charged in 2 hours or less and does not require a cooling-off period. Plus, you can charge your Li-ion battery in 15-30-minute spurts, called opportunity charging.
This allows charging top-ups during breaks or anytime the forklift is idle and supports multi-shift operations with just 1 battery per forklift.
Better Safety
Forklift battery safety is an important factor in forklift operation. OSHA data shows that most battery-related incidents occur during battery moving or watering.
Since lead-acid batteries are composed of 2 high-risk chemicals- sulfuric acid and lead – they pose a safety hazard to operators and the environment. Sulfuric acid can contact and burn the skin or eyes of workers requiring PPE like splash-proof goggles, acid-resistant aprons, face-shield, and rubber gloves.
Lead-acid batteries are also highly explosive and risk explosion while being charged, especially if the charging room isn’t well-ventilated. Among other measures, you also need to install hydrogen sensors in your lead-acid battery storage and charging room(s).
Lithium-ion forklift batteries are different.
Lithium-ion batteries are much safer than lead-acid batteries because they don’t pose as many health risks/hazards.
They’re completely sealed and operators don’t have to open the battery compartment for watering, reducing the danger of electrolyte spills, toxic fumes, or sulfation like in lead-acid batteries.

This also means no PPE is required, reducing the cost of operation and warehouse safety.
In addition, there’s no getting hot with Li-ion batteries because they don’t overheat. Maybe their heat reaches 5 to 6 degrees warmer only.
Less Charging Equipment Required
If you’re using lead-acid batteries, you may need multiple of them per forklift during operations. This may also require you to save their additional storage space.

Additionally, you’ll need to ensure a safe storage environment, away from hot air ducts and other heat sources, away from direct sunlight, and well-ventilated. You must also follow a safe charging process to avoid acid spills or leaks that can cause burns, corrosion, and other hazards.
All these guidelines require trained personnel and resources. But lithium-ion batteries are easy to charge and require little to no maintenance. You don’t need additional storage infrastructure as you don’t need multiple batteries per forklift.
Higher Return on Investment
Lithium-ion forklift batteries last longer than lead-acid batteries.
Whereas a lead-acid battery might last 1,500 cycles under good maintenance, a lithium forklift battery lifespan can last between 2,000 and 3,000 cycles.

Intermittent charging of a few minutes (for instance, 15 to 3 minutes) reduces the lifespan of lead-acid batteries but does not reduce the lifespan of a Li-ion battery.
And, if running lithium-ion batteries in a forklift for 3,000 hours per year, you could achieve an ROI in less than 36 months.
How?
- You don’t need to buy extra batteries (for changeovers) because they charge quickly (allow opportunity charging. This also saves facility space.
- You don’t need more charging stations. Lithium-ion chargers are very small compared to lead-acid, saving on facility space.
- Opportunity charging and fast-charging without damage. You can top up lithium-ion batteries during 15-30-minute breaks (known as opportunity charging). While you can charge a lead-acid battery, it can burn it up and shorten the battery life.
- Less downtime. Opportunity charging helps reduce downtime and increase your fleet’s performance. Also, lithium-ion forklift batteries last 4X longer than lead-acid batteries, increasing your efficiency.
Lithium-Ion Forklift Battery Cons
There aren’t many downsides to lithium-ion forklift batteries. But, no solution is 100% perfect. So, here are the top drawbacks of lithium-ion forklift batteries.
Higher Cost of Acquisition
To be frank, the key con to lithium-ion batteries is the price.

To purchase a lithium-ion forklift battery, you’ll pay $17,000-$20,000 per battery (on average).
The upfront cost of acquiring a lead-acid battery is lower than a lithium-ion forklift battery. The initial investment for a lithium-ion forklift battery may be as much as twice that for a lead-acid battery.
Greater Demand on Electrical Infrastructure
Since Li-ion battery charging is faster, they also require higher input current.
You may need to undertake an energy audit on your facility to understand if you need to revamp your electrical infrastructure to efficiently charge Li-ion forklift batteries.
This will also be a large one-time cost of adopting the Li-ion batteries to power your forklifts.
Hazardous Disposal
Lithium-ion batteries can present various risks or hazards when not handled properly.
This is why the U.S. Department of Transportation monitors the handling, transferring, documenting, and lithium forklift battery disposal.

To safely recycle a lithium-ion forklift battery, it must first undergo a range of safety measures. You can work with your local forklift dealers like Conger to determine where to take your lithium-ion forklift battery for proper disposal.
How to Determine if Lithium-Ion Is the Right Fit
In material handling operations, efficiency and productivity are 2 important keys to success.
Why?
There is only so much time in the day. So, whenever you can find a way to do more in less time, you’ll gain a competitive advantage.
Can a lithium forklift battery offer you that? Here’s what to consider.
Do You Run a Multi-Shift Operation?
Multi-shift applications such as manufacturing, 3PL, food processing, and other 24/7 material handling operations benefit most from lithium-ion batteries. They can use just 1 lithium-ion battery per truck.

Busy, multi-shift operations gain the biggest benefits of switching to lithium-ion forklift batteries
Their only complaint is: we should have switched sooner.
For these multi-shift operations: lithium-ion batteries may be able to pay for themselves in as little as 36 months. For single-shift operations, lithium-ion forklift batteries the ROI timeframe can be longer – 5 years or more.
Do You Have a Freezer/Cold Storage Environment?
Lead-acid batteries don’t handle cold or freezing conditions well. Their capacity can decrease up to 35%.

Lithium-ion forklift batteries maintain their capacity in cold temperatures much better than lead-acid batteries and can be fast-charged in cold temperatures, even inside freezers.
So, operations, where forklifts operate in cold/freezing environments, can quickly benefit from lithium-ion forklift batteries.
Do You Operate On Tight Margins?
If you’re operating in tight margins, you’ll benefit from switching to lithium-ion forklift batteries. Why?
When you switch to lithium forklift batteries, you can reduce energy bills, reclaim real estate and improve productivity. These changes are immediate.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries can be 40% more energy efficient than lead-acid batteries, and 88% more efficient than diesel.
So, lead-acid forklift batteries might be cheaper upfront but are more expensive to own and maintain.
Increased productivity and lower energy bills are just 2 key money-saving reasons to start using lithium-ion forklift batteries.
How to Convert Your Forklifts to Lithium-Ion Batteries
There isn’t anything special required to switch from lead-acid to lithium-ion batteries.
The only retrofit requirement for installing a new Li-ion battery onto the forklift and adding the charge meter to your charging area.
But you need to consider some things before, during, or after the lithium forklift battery installation:
Consider the Weight
Most counterbalanced forklifts comprise the battery’s weight as a component for determining load capacity. With a lighter-weight lithium-ion battery, you may need to add counterweights to maintain a forklift’s nameplate capacity.
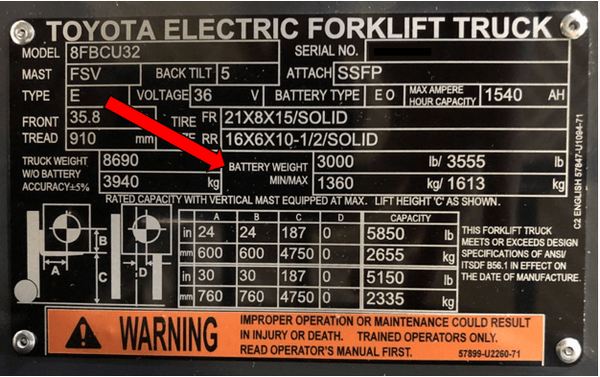
You can also consider changing the specified lifting capacity to accommodate the weight of your new light Li-ion battery. Read more about forklifts in this Toyota Forklift Models: The Complete Guide [FREE Model List].
Consider the Voltage
You need to check, and possibly change the forklift’s battery bank’s charge voltage. Where a low charge voltage will result in incompletely charged forklift batteries, an overly high charge voltage will potentially push the lithium-ion battery outside its permitted operating conditions.
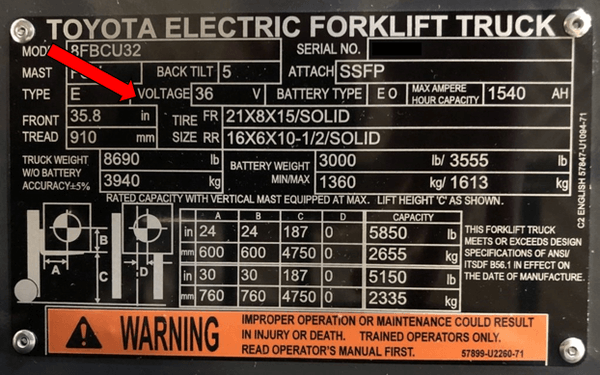
Also, use shunt based, battery monitoring, not voltage based. What does this mean?
Some battery monitoring products use voltage measurement for measuring battery status. In the case of lithium-ion batteries, this can lead to unreliable readings, potentially resulting in deep discharges. So, use only shunt-based (ah counting) monitoring devices that contain a Lithium battery type setting.
Consider the Amp-Hours
Amp-hours measure how much electrical output a battery has.
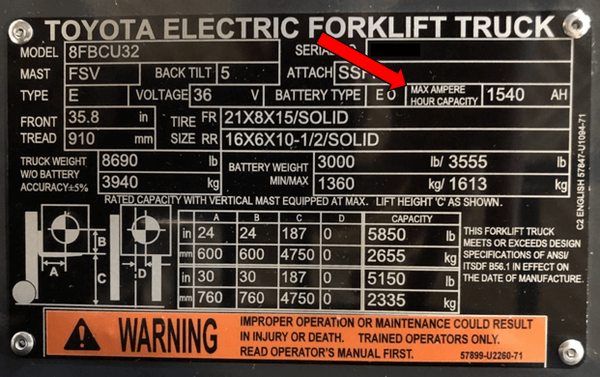
Not every battery has the same amp-hour capacity. And, not every forklift model requires the same amount of amp-hours. So, it’s key to ensure a match between the lithium-ion and forklift amp-hours.
Consider Culture Change
To get the most out of your Li-ion forklift battery, train your operators to rigorously employ opportunity charging. Whenever the forklift is scheduled to be idled for some amount of time, they should remember to plug it in!
Lithium Forklift Batteries: Everything Else You Should Know
The Main Lithium Forklift Battery Types
There are multiple types of lithium forklift battery types available in the market.
They depend on the type of cathode material used in them. The common lithium forklift battery options include:
- Lithium cobalt oxide
- Lithium manganese oxide
- Lithium iron phosphate (LFP)
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is the most popular lithium forklift battery type in the modern material handling industry. It offers higher safety, and current and has a lower environmental impact than other types of lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium Forklift Battery Sizes
Selecting the right battery size is essential to ensure that your forklift can perform at its peak.
There are many different forklift battery sizes, depending on your lift truck’s size, brand, make, and model. In general, the larger the forklift you operate, the larger the battery size.

Often, you can find the size displayed on the battery’s nameplate. If it’s missing here, check the cell connectors nearest to the positive terminal, where you’ll find the model number, serial number, and weight.
When selecting the battery, consider the lithium forklift battery weight against the forklift model.
Overall, forklift batteries can weigh 600 lbs. to 5,000 lbs.+ for the biggest electric lift trucks.
Important Lithium Forklift Battery Specs
There are some important battery specs you may want to look out for when shopping for a lithium-ion forklift battery:
- Type of forklift truck it will be used on (different classes of forklift types)
- Charging duration
- Charger type
- Amp-hours (Ah) and output or capacity
- Battery voltage
- Battery compartment size
- Weight and counterweight
- Operating conditions (e.g. freezing, high-intensity environments, etc.)
- Rated power
- Manufacturer
- Support, service, and warranty
Lithium Forklift Battery Charging
Fully charging a lithium-ion forklift battery from zero to 100% takes just under 2 hours.

The charge and use cycle for a lithium forklift battery is a 1 to 1.2-hour full battery charge, 8 hours of use, and another 1 to 2-hour full battery charge.
Also, the Li-ion forklift battery should always be left on charge (or charged) when not in use. It won’t overcharge because of the onboard computer controllers that monitor charging and will shut it down once it’s charged.
Required Lithium-Ion Forklift Battery Charging Equipment
The key aspects of Li-ion forklift battery charging are:
- Check whether you’re using the right charger with the right power output. Lithium forklift battery chargers are specialized.
- Some lithium forklift battery chargers are the size of a shoe box and can weigh as little as 20 lbs. This allows them to be placed wherever an operation runs power and is most convenient.
- The small size of stand-alone or wall-mounted lithium battery chargers means a smaller footprint and easy relocation.
- Check the voltage range (12V, 24V, 36V, 48V, 72V, and 80V).
- Make sure the lithium battery charger is programmed to provide the recommended Ah output corresponding to the battery capacity and charging rate.
- If the lithium battery has a dual plug, it can be charged in half the time but this requires special charger models.
- Check and ensure that the facility’s electric infrastructure can safely supply enough power to support the forklift charging.
- Check charger cables are in good working order. Also, check if the connectors are damaged or cracked. If so, they’ll need to be replaced.
- Lithium-ion batteries don’t require water checking.
- Clean the battery once a month as chemical build-up can corrode the tray and void the warranty
- Lithium forklift batteries don’t need cooling after charging.
The Charging Process for Lithium-Ion Forklift Batteries
- Park the forklift truck in a designated place.
- Set the parking brake.
- Turn off the forklift.
- Wear the right PPE.
- Check and make sure the charger is turned off.
- Plug the charger into the forklift, and turn it on (you can plug it in with 2 hands).
For a full charge, let the battery charge for up to 1 ½ to 2 hours until it’s fully charged.
For opportunity, charge and remove the charger once your break is finished (after 10 to 45 minutes). Opportunity charge is the quick charge during breaks, shift changes, or determined by the shift schedule (but doesn’t have to be scheduled).
Lithium forklift batteries have a battery management system (BMS) that controls their every aspect: amperage, voltage, and temperature. So, once the battery is plugged into the charging system, the BMS ensures that it charges safely.
Lithium Forklift Battery Maintenance Requirements
Lithium forklift batteries are virtually maintenance-free. They don’t require constant watering, equalization charging, or cleaning.

But they’re not completely “set and forget” either.
Here’s a simple lithium forklift battery maintenance checklist:
- Do not leave Li-ion batteries unused for extended periods, either in the forklift or in storage.
- When a Li-ion forklift battery has been unused for 6 months or more, check the charge status and then charge or dispose of the battery as appropriate.
- When using the Li-ion forklift battery, routinely check its charge status.
- Always follow the appropriate charging instructions provided by the Li-ion forklift battery manufacturer as contained in its product’s user manual.
- You will not need to perform a lithium forklift battery equalization charge.
- You will not need to install a lithium forklift battery watering system because it’s sealed.
- Never recharge or use a battery that’s been damaged, and don’t expose one to high heat.
- Closely monitor your lithium forklift battery nearing its end of estimated life to avoid attempts of charging damaged batteries.
- Consider replacing the lithium battery if you note that its run time drops below about 80% of the original one or that its charge time increases significantly.
Lithium-ion batteries have no serviceable parts inside, so don’t try to tinker with one. If you think your lithium forklift battery needs replacement, contact a reputable vendor like Conger Industries for help.
Lithium Forklift Battery Storage
Here are some important considerations for lithium forklift battery storage:
- Never store lithium-ion forklift batteries when they’re fully charged or fully discharged. Instead, discharge or charge the battery to approx. 50% capacity before storage.
- If stored for a long time, charge the lithium-ion forklift battery to about 50% capacity at least once every 6 months.
- Store a forklift battery separately from the forklift (remove and store separately).
- Store the lithium-ion battery at mild, dry temperatures between 41 °F and 68 °F (5 °C and 20 °C), not at high temperatures.
- Store lithium batteries away from sunlight, heat, and humidity.
- Keep the storage area well-ventilated and dry, and maintain the temperature relatively steady.
- When stored, keep the lithium battery’s terminals from touching and not in contact with any metals or other battery terminals. Use battery terminal covers where applicable.
- Separate batteries by age and type. This helps prevent the ends from touching and keeps those near their end of life away from new ones.
- For maximum safety of your lithium battery, use a battery storage cabinet. It provides the needed environment for battery storage as well as insulation and fire suppression to prevent hazardous lithium-ion battery fires.
Frequently Asked Lithium Forklift Battery Questions
Do Forklifts Use Lithium Batteries?
More operations are using lithium-ion batteries to power their electric forklifts. Multi-shift applications such as food processing, manufacturing, 3PL, and other 24/7 material handling operations benefit most from lithium-ion industrial forklift batteries.
Operations where forklifts work in cold environments also quickly benefit from lithium-ion batteries. They can be fast-charged in cold temperatures (even freezers) and maintain their capacity in cold temperatures.
Although lithium batteries have a high initial cost, in the long run, you can save on the following in the long run:
- Longevity: A lithium-ion battery can last 2 to 4X longer than a lead-acid battery
- Energy bills: Lithium forklift batteries are 30% more energy-efficient and charge 8X faster than lead-acid batteries.
- Downtime: Lithium batteries can be opportunity-charged during operator breaks and don’t need to be swapped, saving downtime and longer run times.
- Labor costs: These batteries don’t require maintenance, watering, or equalizing.
- Productivity: Longer run times result in better efficiency and productivity.
- Real estate: With lithium forklift batteries, you can reclaim the charging area and use it for additional storage.
How Much Does a Lithium Forklift Battery Cost?
A lithium forklift battery can cost $25,000+ per battery. The costs range between $17,000 and $25,000 per forklift battery, more expensive than lead-acid batteries – about 2 to 2 1/2.5X more.
What Is the Biggest Advantage of a Lithium-Ion Forklift Battery?
Increased runtime and more productivity. This is because Li-ion batteries don’t lose power like lead-acid and since they can charge quicker (opportunity charge). But lithium-ion batteries are also cost-effective and return the RIO in the long run because of increased efficiency, reduced costs (electricity and labor), and improved productivity.
What Is the Biggest Disadvantage of a Lithium-Ion Forklift Battery?
The cost is the biggest downside of lithium-ion forklift batteries. And it may not make sense financially yet for smaller operations to switch to them. After all, a lithium-ion battery costs about $17,000 to $25,000 depending on manufacturer or use.
How Long Does It Take to Charge a Lithium-Ion Forklift Battery?
A lithium-ion forklift battery can charge up to 80% in an hour. But Li-ion batteries can also charge throughout the day in 15- or 30-min spurts or fully charge in 1 to 2-hour continuous sessions. Compared to the 8-hour charge time plus an additional 8-hour cooldown time for a lead-acid battery, lithium-ion batteries are more efficient.
Is It Okay to Leave a Lithium-Ion Battery on the Charger?
Leaving a lithium-ion battery on a charger is okay. The batteries generally have onboard computer controllers that monitor charging and will shut down once they’re charged. This helps stop overcharging.
Can a Lithium Forklift Battery Be Overcharged?
It’s possible for a lithium forklift battery to be overcharged, though it rarely happens. Lithium forklift battery charges to full charge in between 1 to 2 hours. Once plugged in, it won’t overcharge because of the onboard computer controllers that monitor charging and will shut it down once it’s charged.
Can a Lithium Forklift Battery Be Over-Discharged?
Most lithium-ion forklift batteries have a depth of discharge ranging from 80% to 100%. Avoid over-discharging a lithium battery because doing so can potentially cause individual cells to discharge at different states, resulting in the battery’s permanent damage.
What Is the Average Lithium Forklift Battery Operating Temperature?
Lithium batteries can operate in nearly any environment, with temperatures ranging from -4° F to 130° F. That said, the optimal operating temperature range is between 50° F and 110° F.
This allows the Li-ion forklift battery to operate at peak performance while preserving its longevity and function at the highest capacity for even up to 6,000 cycles. Because when you operate in extreme conditions – very cold or very hot – the battery starts to wear, shortening its life span.
Do Lithium Batteries Get Worse Over Time?
Lithium-ion batteries have a limited life span of about 2,000 to 3,000 charging cycles, while some go up to 6,000 cycles. They will gradually lose their capacity to hold a charge due to aging, and this is irreversible. As the Li-ion battery ages and loses capacity, the run time also decreases.
Can a Lithium Battery Last 20 Years?
Some lithium battery manufacturers are claiming that lithium-ion batteries can last 20 years. But given their limited adoption and use, the jury is still out.
What Kills a Lithium Battery?
Lithium batteries are naturally degrading. But they can sometimes die instantly. Heat is the leading killer of lithium batteries. High or low temperatures can kill lithium batteries. The effects of too much increased or reduced temperature can kill the battery’s cells and result in killing it entirely.
How Do You Prolong the Life of a Lithium Battery?
Here are some top tips for prolonging the life of your lithium forklift battery:
- Minimize exposure to high temperatures during use or storage
- Minimize exposure to low temperatures, especially when charging
- Use the correct battery charger when charging
- Avoid physical tampering or damage
Conclusion
That’s it: You now know everything you need to know about lithium forklift batteries.
![Lithium Forklift Batteries: The Complete Guide [Pros, Cons, Costs]](https://www.conger.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Lithium-Forklift-Batteries-The-Complete-Guide-Featured-Image-final.jpg)